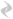AllWave Flex-bend optimized fiber G.657

FTTX, HFC and high density fiber optic systems require connectivity system that provides stable and highly reliable optical performance. AllWave Flex is the first new fiber that offers outstanding bend-performance for FTTX, enterprise network and wherever small bend parameters may be encountered. To meet that challage, Cellco offers jumpers, pigtails and pre-assembled patchpanels with very low bending loss according to G.657 requirements. Features and Benefits:
• 5 times lower bending loss than conventional single-mode fiber (CSMF) pigtails, • 50% lower connector loss than CSMF pigtails, • Zero Water Peak, low loss performance in 1260 to 1650 nm wavelengths. • Fiber superior to and compliant with ITU G.652D specifications • low attenuation at bend radius as small as 10 mm. • zero water peak ( ZWP ) supports CWDM in the E-band. • ideal for transmission in C and L bands. • offered for evolving FFTX applications. The comparison of Allwave Flex fibers with competitors fibers - the impact of bending (on a core with X mm diameter) on attenuation: 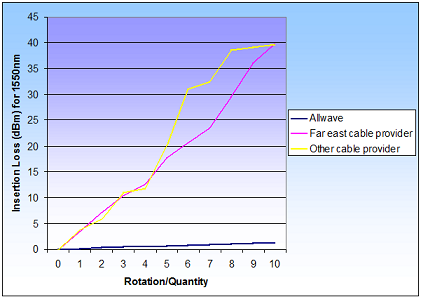
source : Cellco, Quality Eng. TrueWave REACH Fiber– G.656
The new trend in development of optical fiber leads to the creation of maximally universal optical fibers which comply with the requirements of various types of transmission and data formats. The new ITU G.656 recommendation is a good example of this trend. The standard in question derives from G.655 and it defines the requirements for fibers which combine advantages of the most popular standards, namely G.652 (G.652d- the latest requirement from G.652 series) and G.655 (g.655c). The first fiber to comply with the requirements of G.655 is TrueWave Reach, developed by OFS (previously Lucent, AT&T). The new Non-Zero Dispersion fibers of G.656 standard are to enable telecommunication operators to send the CWDM signal on greater distances without the need for chromatic dispersion compensation. The ITU recommendations define the new requirements for fibers, which are to boost development of optical networks. According to these standards, fibers are to meet the demands of CWDM and DWDM systems, providing wider usable transmission band. The usage of this type of fibers both enables to avoid dispersion compensation in CWDM systems and brings at least 40 channels increase in DWDM systems. The new standard determines dispersion value not only in the 1530-1565nm band (as in case of G.655, value 1-10ps/nm*km) but also in a broader band of 1460-1625 nm (value 2-14ps/nm*km). The maximum value of polarization mode dispersion has also been defined. AllWave Fiber – G.652d AllWave® G.652d is currently one of the best standard single mode optical fibers. It can be used all the way along 1280-1625 nm band. The fiber has very low attenuation in so called 'water peak', eg. for 1383 nm attenuation does not exceed 0,3dB/km. AllWave fiber complies with ITU-T G.652 D standard. AllWave single mode fiber is also the first fiber designed for operation of optical systems along the whole 1280-1625 nm band. Earlier, optical systems making use of single mode fibers could operate only in the second optical fram, i.e. 1310 nm (band 0) or in C and L bands (1530-1625 nm). AllWave has made available the E band (~1400 nm) and S band (1460-1530 nm). Special production process had eliminated water peak, which extended the usable band by about 100 nm. Features Fully compatible with international standards;  The leader of its class- low attenuation in the band 1260-1625 nm;  Increases the usable band by 50%, enabling for operation of both 16-channel CWDM systems and future DWDM systems, which work within all bands;  The best in its class - low PMD;  Dlux TM is higly resistant to environmental conditions and easy to strip; TrueWave RS Fiber – G.655c TrueWave®is compatible with ITU-T G.655c standard (NZDF- Low Water Peak). TruWave RS offers lower dispersion as it works in a wider band, also in DWDM systems, both in the C (1530-1565 nm) and L band (1565-1625 nm). Low dispersion of TrueWave RS fiber increases network capacity and dicreases the costs of creation and operation of the system, mailny because it simplifies compensation of dispersion. Low dispersion along with low gradient allows for wider transmission range without the need for compensation of this parameter in networks working on speed of 2,5 or 10Gbit/s. These parameters become important when it comes to network development and movement in the direction of systems with 40Gbit/s. Chromatic dispersion is a parameter which changes its value according to the wavelength. This change is proportional to the gradient of dispersion causes smaller changes of dispersion in the bands used by transmission systems. In case of multichannel DWDM systems it helps to unify the solutions for the individual bands, at the same time dicreasing the costs of creating a transmission system. Another merit of low gradient is that it helps to avoid the phenomenon of Four Wave Mixing, which may emerge at the lower end of the characteristic when the chromatic dispersion value is too low.
Features Low dispersion value both in C and L bands;  The possibility of wide transmission range without the need for dispersion compensation;  Parameters of this fiber enable for implication for future optical networks, making use of OXC optical patchpanels and high output, such as 40Gbit/s;  Low tendency towards attenuation change when bending even the 1625 nm wavelength;  The first fiber designed for L band, both in terms of its attenuation and dispersion; |